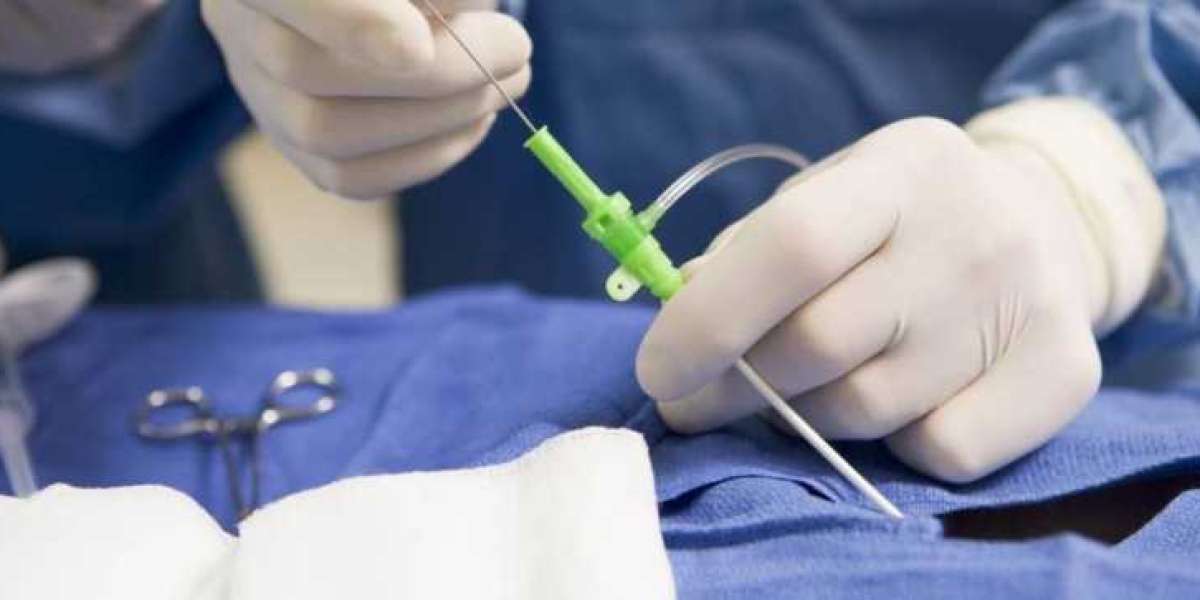
Coronary artery disease is a prevalent heart condition that drastically impacts the lives of numerous individuals. The main blood vessels that supply the heart with oxygen, nutrients, and blood are unable to adequately supply the heart muscle as a result of this disease.
Coronary artery disease is typically caused by cholesterol deposits in the heart arteries and inflammation. To visualize blood vessels, physicians primarily rely on angiography, a medical imaging technique.
The heart is deprived of sufficient oxygen-rich blood, which results in the development of signs and symptoms of obstructed arteries. Reduced blood flow to the heart can lead to chest pain and shortness of breath if you have coronary artery disease. A heart attack may result from a complete obstruction of blood flow.
In reality, you may experience chest pressure or discomfort. According to some people, it's like someone's standing on their chest. The chest pain is predominantly felt on the left or middle side of the chest. Angina can be precipitated by the expression of intense emotions. Fortunately, the pain typically subsides within minutes of the triggering event concluding.
The pain in the neck, arm, or back of some people, particularly women, may be brief or sharp. You may experience an unusual level of fatigue if the heart is unable to adequately circulate blood to satisfy your body's requirements.
A heart attack is an additional significant symptom of obstructed arteries that you should be aware of. A coronary artery that is entirely obstructed will lead to a heart attack. Crushing chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, sweating, and shoulder or arm pain are the classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack. Women are more likely to experience symptoms that are less common, including fatigue, nausea, and neck or jaw pain.
Therefore, when should you consult with a physician and undergo an angiography? Call 911 or your local emergency number immediately if you suspect that you are experiencing a heart attack. For those who are unable to access emergency medical services, it is recommended that they have a designated driver transport them to the nearest hospital. As a last resort, only drive yourself to the hospital.
Having a significant family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or smoking increases the likelihood of developing coronary artery disease. If you are at a high risk of developing coronary artery disease, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. Additionally, tests such as angiography may be required to evaluate for coronary artery disease and narrowed arteries.
Поиск
популярные посты